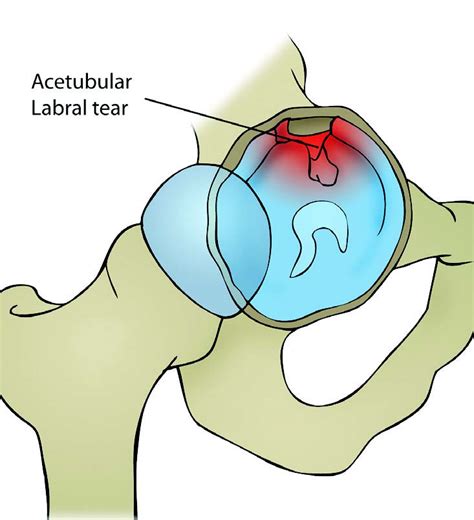
acetabular labral tear special tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology : OEM A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question. Yes I understand this but I want to find out if it’s possible basically go from a single ingredient split the chain so the ingredient goes into autoclaves in order to keep my entire line at one tick .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Please select the CORRECT statement regarding autoclaving and freezing. A) Autoclaving kills any microbes in a sample, sterilizing it; freezing inhibits the growth of microbes in a sample but may not kill all of them.
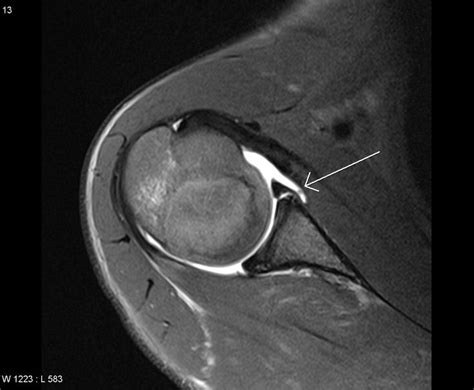
The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabul.The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.
Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging. Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.
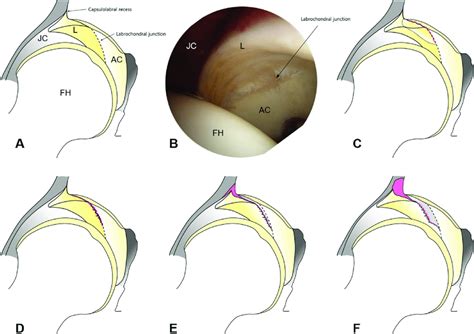
Various clinical tests have been described, but little is known about their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An acetabular labral tear is a diagnostic challenge. This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic. Clinical examination should consider lumbopelvic and extra-articular pathologies in addition to intra-articular pathologies when assessing for the source of symptoms and functional limitation. If a labral tear is suspected, further diagnostic testing may be indicated.
Arthroscopy remains the reference standard for diagnosing acetabular labral tears allowing for dynamic examination and assessing the extent of the tear [50, 52]. However, it is more invasive and may have limited access to posterior labral tears depending on portal positioning [52].The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.
Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging.
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.Various clinical tests have been described, but little is known about their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An acetabular labral tear is a diagnostic challenge. This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic.
right superior acetabular labral tear
Clinical examination should consider lumbopelvic and extra-articular pathologies in addition to intra-articular pathologies when assessing for the source of symptoms and functional limitation. If a labral tear is suspected, further diagnostic testing may be indicated.
labral tear mri images
Autoclaving is a sterilization method that uses high-pressure saturated steam at 121°C for typically 15-20 minutes to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including spores. It is commonly used in .Autoclaving is preferred over dry heat because it can effectively be used to sterilize a wide variety of items, including liquids, powders, metal instruments, and glassware. When autoclaving solid items, they should be wrapped in foil .
acetabular labral tear special tests|acetabular labral calcification radiology